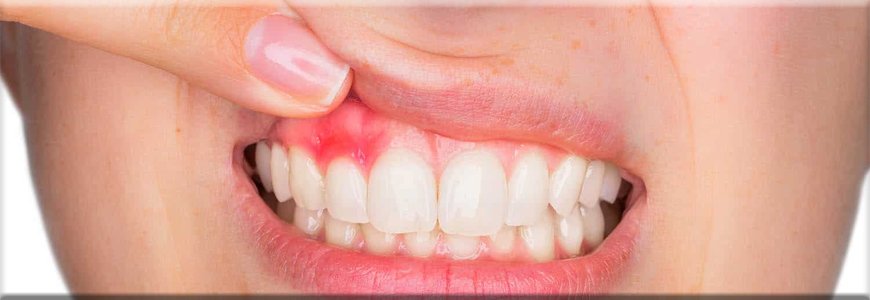
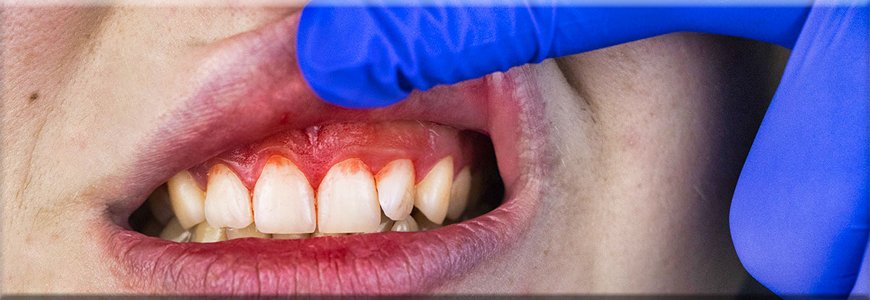
What is the most common gum problem?
Gum problems, also known as periodontal diseases, are prevalent worldwide and can manifest in various forms. However, one of the most common gum problems is gingivitis. Gingivitis is characterized by inflammation of the gums, typically caused by plaque buildup along the gumline. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth when sugars and starches from food interact with the bacteria in the mouth. If not removed through proper oral hygiene practices such as brushing and flossing, plaque can irritate the gums, leading to inflammation.
The primary symptoms of gingivitis include red, swollen gums that may bleed easily, especially during brushing or flossing. Additionally, individuals with gingivitis may experience bad breath or a bad taste in the mouth due to the presence of bacteria in the oral cavity. While gingivitis itself is generally not painful, if left untreated, it can progress to a more severe form of periodontal disease known as periodontitis.
Periodontitis is characterized by the destruction of the tissues surrounding the teeth, including the gums, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone. As the disease progresses, pockets may form between the teeth and gums, which can harbor even more bacteria and exacerbate the condition. Without intervention, periodontitis can eventually lead to tooth loss and may even contribute to systemic health issues such as heart disease and diabetes.
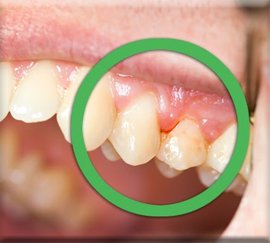
Other common gum problems include:
Gum Recession: This occurs when the gums pull away from the
teeth,
exposing the tooth roots. Gum recession can be caused by periodontal
disease, aggressive brushing, or genetic factors.
Gum Abscess: A gum abscess is a pocket of pus that forms due to a bacterial infection. It can cause pain, swelling, and redness in the affected area.
Gum Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience heightened sensitivity in their gums, which can be triggered by factors such as hot or cold temperatures, acidic foods, or brushing too hard.
Gum hyperplasia: This condition involves an overgrowth of gum tissue, which
can be caused by certain medications, hormonal changes, or underlying health
conditions.
Gum ulceration: Ulcers in the gums can be caused by trauma, irritation, or
systemic conditions such as Crohn's disease or herpes infections.
Preventing gum problems requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, as well as lifestyle modifications such as avoiding tobacco use and maintaining a healthy diet. Early detection and treatment of gum problems are crucial for preventing further complications and preserving oral health. Therefore, individuals should be vigilant about any changes in their gum health and seek professional dental care if they notice any concerning symptoms.